- Address Translation Architecture

- Implementation of Page Table
* Page table은 main memory에 상주
* Page-table base register(PTBR)가 page table을 가리킴
* Page-table length register(PTLR)가 테이블 크기를 보관
* 모든 메모리 접근 연산에는 2번의 memory access 필요
* page table 접근 1번, 실제 data/instrudction 접근 1번
* 속도 향상을 위해 associative register 혹은 translation look-aside buffer(TLB) 라 불리는 고속의 lookup hardware cache 사용
- Paging Hardware with TLB

- Associative Register
Associative registers(TLB): parallel search가 가능
* TLB에는 page table 중 일부만 존재
Address translation
* page table 중 일부가 associative register에 보관되어 있는 경우
* 만약 해당 page#가 associative register에 있는 경우 곧바로 frame #를 얻음
* TLB는 context switch 때 flush(remove old entries)
- Effective Access Time
* Associative register lookup time = e
* memory cycle time = 1
* Hit ratio = a
* associative register에서 찾아지는 비율
- Effective Access Time (EAT)
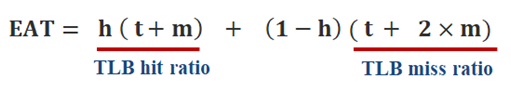
- Two-level Page Table
* 현대의 컴퓨터는 address space가 매우 큰 프로그램 지원
* 32 bit address 사용시 : 2^32(4G)의 주소 공간
* page size가 4K시 1M개의 page table entry 필요
* 각 page entry가 4B시 프로세스당 4M의 Page table 필요
* 그러나, 대부분의 프로그램은 4G의 주소 공간 중 지극히 일부분만 사용하므로 page table 공간이 심하게 낭비됨
* 시간도 손해, 공간도 손해 but 사용하지 않는 주소 공간 문제 해결 가능
-> page table 자체를 page로 구성
-> 사용되지 않는 주소 공간에 대한 outer page table의 엔트리 값은 NULL(대응하는 inner page table이 없음)
- Address-Translation Scheme
* 2단계 페이징에서의 Address-translation schema

'CS STUDY > OS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 18. Memory Management 4 (0) | 2023.09.15 |
|---|---|
| 17. Memory Management 3 (0) | 2023.09.14 |
| 15. Memory Management 1 (0) | 2023.09.09 |
| 14. deadlock2 (0) | 2023.09.08 |
| 13. Deadlock 1 (0) | 2023.09.07 |



